Punjab Agriculture university
High-throughput Genotyping Analysis Facility for Application of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology in Agriculture, Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana
The Bioinformatics Center at PAU, Ludhiana, is dedicated to the comprehensive analysis of various Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) data from an agricultural perspective. The center's primary goals include analyzing the genomes and transcriptomes of major field crops to identify economically important genes related to biotic and abiotic stress tolerance, productivity, and quality improvement. Additionally, the center focuses on studying the genomes and transcriptomes of plant pathogens to understand evolutionary patterns, developing databases for comparative analysis using in-house and publicly available datasets, and creating deep-learning/machine learning-based software for stress-tolerant gene annotation. The center is also involved in mining genes related to stress tolerance and developing associated markers, applying computational approaches in the crop breeding programs of major field, fruit, and vegetable crops. The Center is contributing to human resource development in bioinformatics.
Among its accomplishments, the center has pioneered the creation of the first online database on plant disease susceptibility genes, aiding in target selection for gene knockdown and the development of disease-resistant crops. They have also designed GUI-based software for small genome assembly and annotation. In addition to its research activities, the center annually provides hands-on bioinformatics training to 5-7 undergraduate students as part of its skill development program (Figure 3). Several software and databases developed by the center are publicly accessible at http://45.248.163.59/bic .
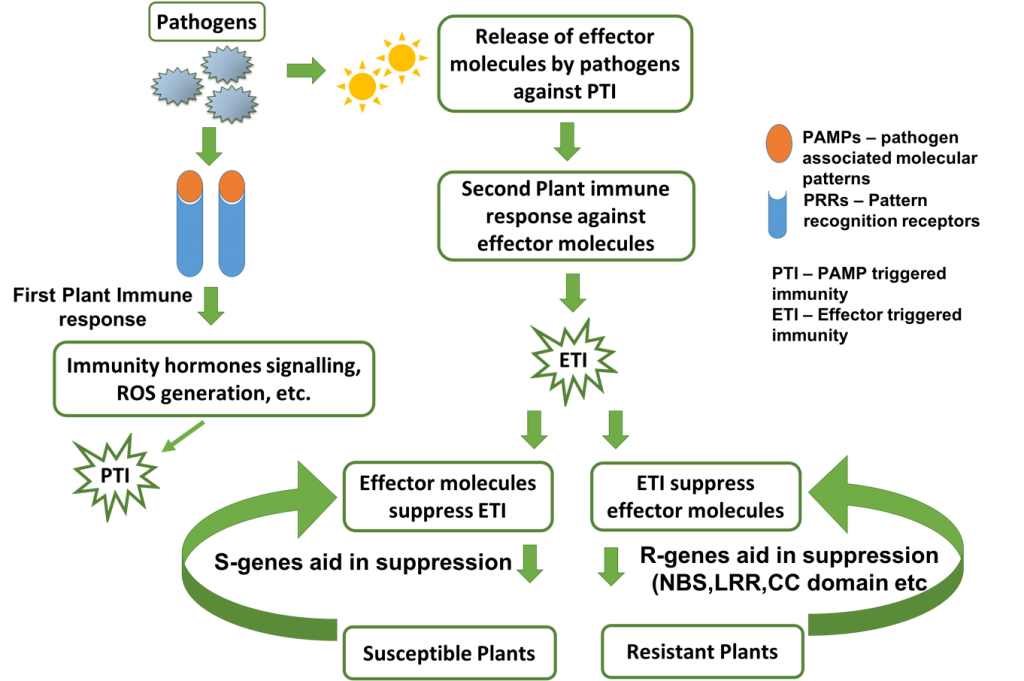
Overview of the mechanism of plant immune response
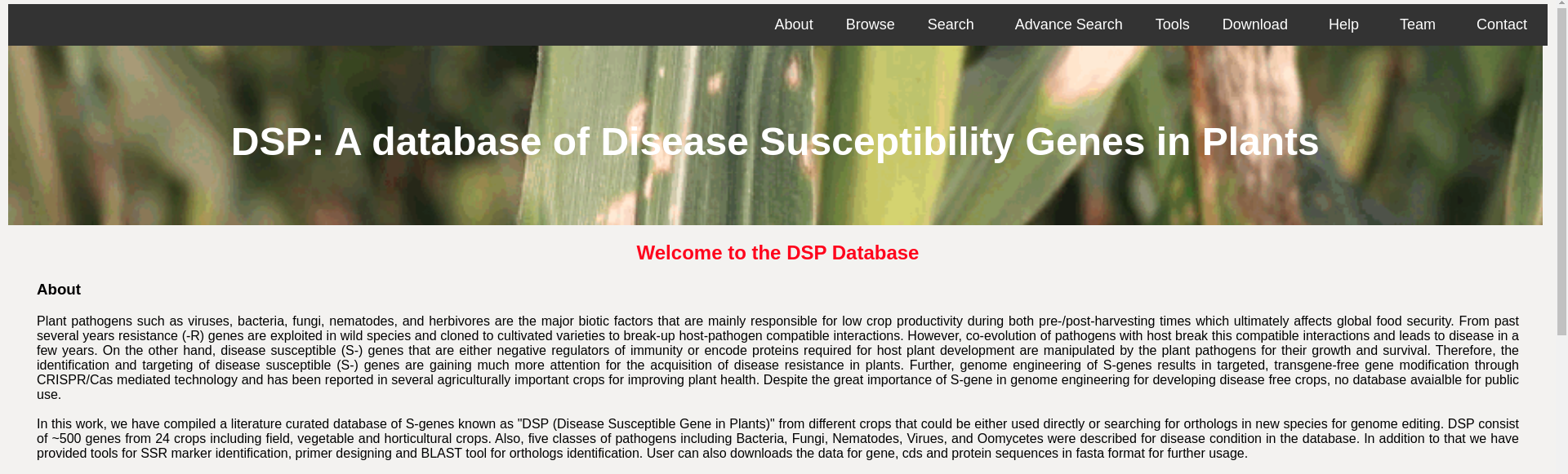
Home page of the DSP database
With expertise in Next-Generation Sequencing data analysis, the center is actively engaged in developing tools and databases of agricultural significance. The advent of NGS technologies has revolutionized genotyping, generating vast genomic datasets that necessitate dedicated computational and storage capabilities. There are several advances in bulked segregant analysis-based strategies from large populations at high read depth, estimating delta SNP index to identify genomic region associated with important quantitative trait including methods viz. QTL-seq, BSA-seq, etc. Of the few pipelines available for analysis of such type of data, most of them are complex to understand for students or researchers who have little background in bioinformatics.
The center is at the forefront of high-throughput genotyping data generation for various crops to analyze samples from vegetable and field crop genomes. The overarching objective is to establish a computational facility focused on developing smooth pipelines for analysis of high-throughput genotyping data in targeted crop plants, simultaneously providing training opportunities for young students and researchers in data analysis.


The Bioinformatics Center at PAU has organized a One-day symposium entitled "Recent Trends in Vegetable and Fruit Genomics” on 9th March 2022
