CSIR-NEIST, Jorhat
Bridging the Technological Gap: Bioinformatics Initiatives for Drug Discovery and Healthcare Innovation at CSIR-NEIST, Jorhat
The Bioinformatics Center at CSIR-NEIST is focused to developing indigenous open-source software for drug discovery, aiming to bridge the significant technological gap in our country. The center focuses on developing open source software for computational drug discovery, disease-specific web portals, clinical data repositories, computer-aided drug design, molecular modeling, NE biodiversity, traditional knowledge, machine learning, data science applications in food and nutrition, as well as databases, computing, modeling, and informatics.
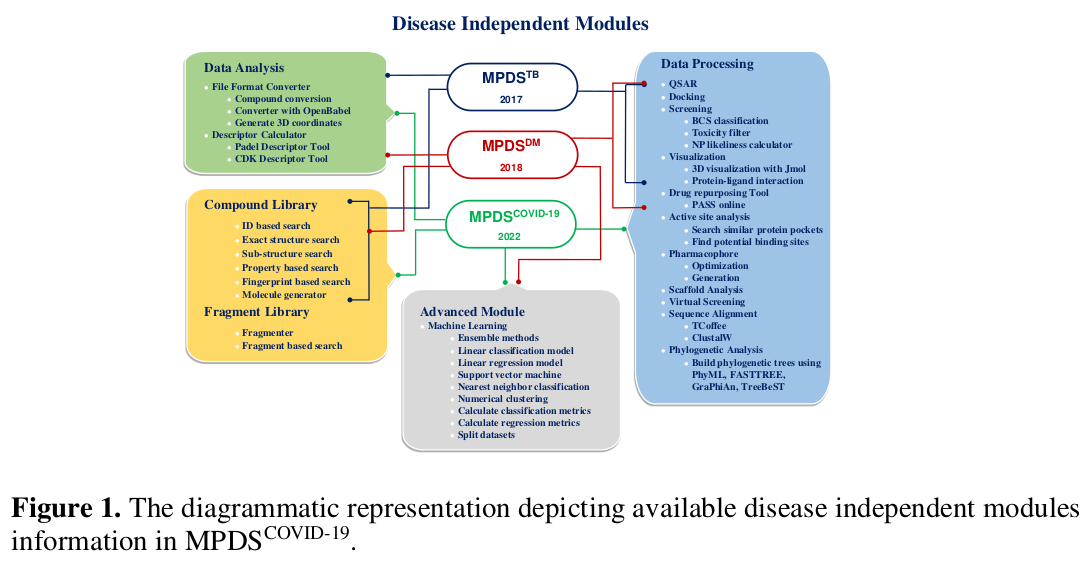
With expertise in Bioinformatics, Artificial Intelligence, and Machine Learning, the center addresses complex problems in areas of natural sciences. The Molecular Property Diagnostic Suite (MPDS) is a widely used open-source Computer-Aided Drug Design (CADD) software, forming a robust foundation for individuals contributing to drug discovery research in Atmanirbhar Bharat (Figure1). The center adeptly integrates chemoinformatics, bioinformatics, and molecular modeling to solve challenges. Multiple machine learning models have been developed for tasks such as antiviral prediction and clinical trial prediction. The center has also established various web servers and databases, accessible at , http://acds.neist.res.in/a2idv2 , https://acds.neist.res.in/cadv2 , https://neist.res.in/osadhi , and https://neist.res.in/neimpdb . The MPDS, a product of the center, is widely utilized by the global scientific community.

The BIC center has successfully conducted numerous workshops and seminars and trained students in software development and machine learning applications for drug discovery challenges. Equipped with a powerful computational infrastructure having a capacity of 200 TF, the center's servers and workstations have 10th Gen scalable processors, 32 GB of GPU, and essential hardware, enabling cutting-edge bioinformatics research.
By establishing effective collaborations with prime institutes like CSIR-IITR, CSIR-IGIB, JNU, and CSIR-CLRI having diverse expertise in genomics, toxicology, molecular modeling, machine learning, and data sciences for National Network Project (NNP), the center proposes establishment of a digital repository, The DISHA initiative, which seeks to bridge the gap between medical doctors, research scientists, and patients. This initiative aims to innovate ‘Research in Medicine’ by fostering effective collaboration between medical professionals and scientists, identifying fundamental healthcare issues, and devising solutions to address them.

